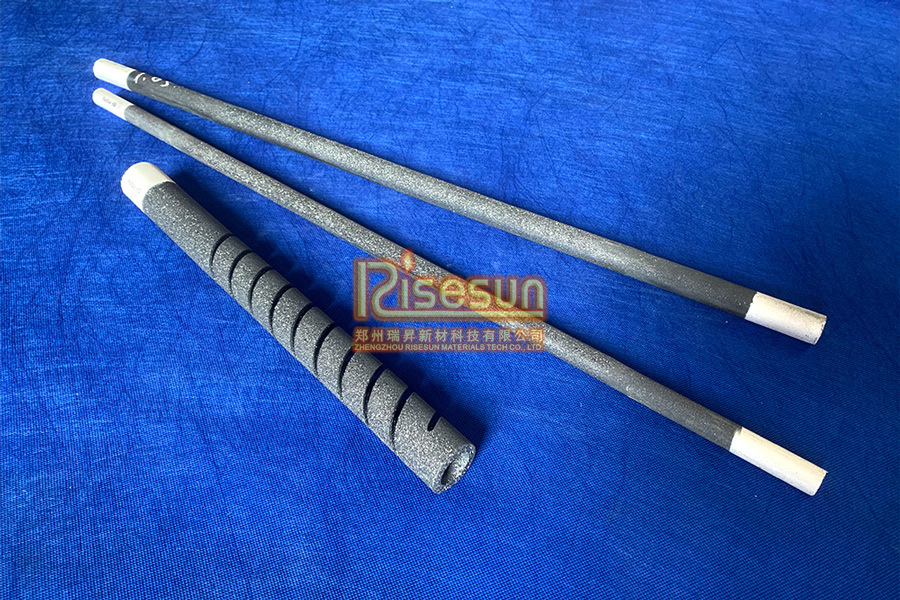
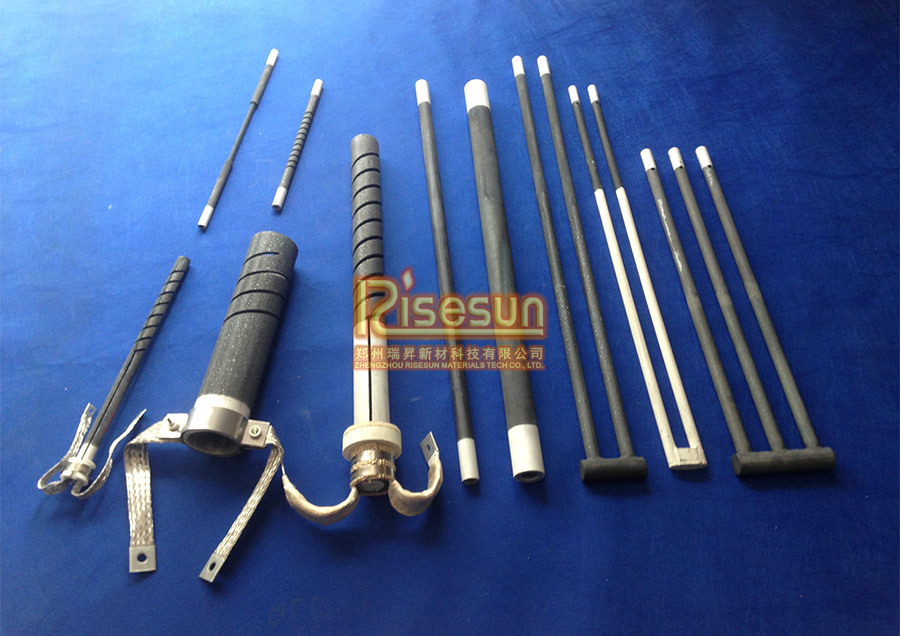
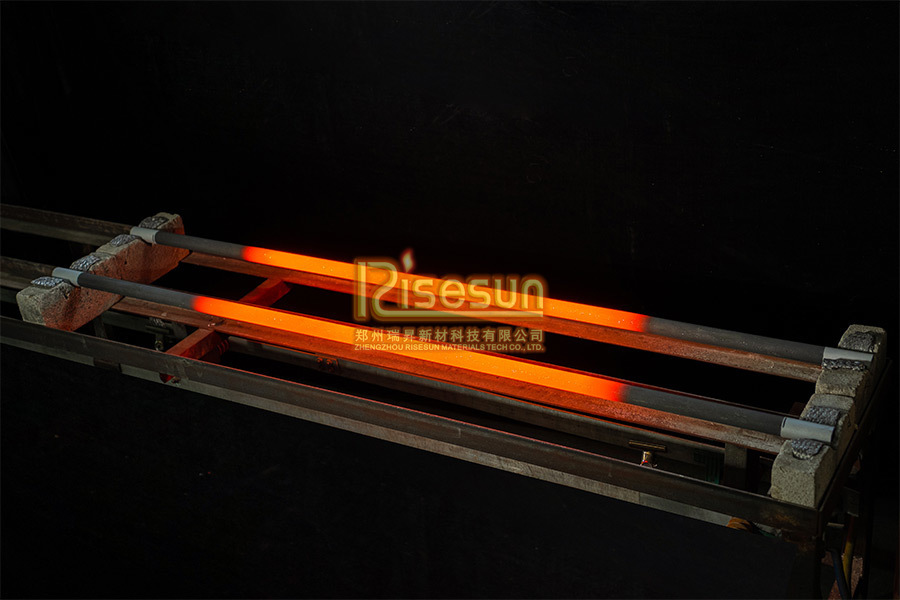
|
Atmosphere
|
Impact on Element
|
Solution
|
Coating
|
|
Vapor and moisture
|
The service life is about 20% shorter than that in the dry air.
|
New furnaces or furnaces unused for a long time should be thoroughly dried at low temperature before heating.
|
A coating
|
|
Nitrogen
|
Nitrogen reacts with SiC above 1,400℃, producing silicon nitride, making elements fragile and shortening the service life of elements. This is affected by dew point in the same way as H2.
|
The recommended furnace
temperature is not higher than 1300℃ with surface loading as low as possible.
|
B coating
|
|
Hydrogen
|
When elements are heated to above 1,350℃, their resistance will increase rapidly and their mechanical strength will decline, furthermore, the service life of elements varies greatly, depending on the moisture content of gas.
|
The recommended furnace
temperature is not higher than 1300℃ with surface loading lower than 5W/cm2
|
C coating
|
|
Ammonia
|
Same as hydrogen and nitrogen
|
The recommended furnace
temperature is not higher than 1300℃ with surface loading lower than 5W/cm2
|
B coating
C coating
|
|
Disassociated gas(N2,CO,CO2,H2,CH4)
(N2, CO, CO2, H2, CH4)
|
Decomposed Carbon black attach to body of heating elements to make elements loose.
|
Convey air into furnace
frequently to burn up additional
Carbon. For furnace design,
keep enough space between
elements and elements to prevent short circuit.
|
|
|
Sulphur
(S、S2)
|
When elements are heated to 1,300℃, their surfaces will be eroded, leading to a sharp increase in resistance.
|
Control the element temperature to below 1,300℃.
|
|
|
Vacuum
|
SiO protective film will not be formed in high vacuum, and Silicon carbide will be decomposed itself, then service life of elements will be shortened.
|
Furnaces temperature lower than 1000℃ with pressure above 0.13Pa.
|
|
|
Others
|
Various substances from treated materials, such as Pb, Sb and alkali metal, react with elements, which may shorten the service life of elements.
|
To get rid of these substances in advance, set up a gas exhaust in furnace to reduce the impact.
|
D Coating
|